All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Just as with a fixed annuity, the owner of a variable annuity pays an insurer a round figure or series of settlements for the promise of a series of future settlements in return. However as discussed above, while a dealt with annuity expands at an ensured, constant rate, a variable annuity expands at a variable rate that depends upon the performance of the underlying financial investments, called sub-accounts.
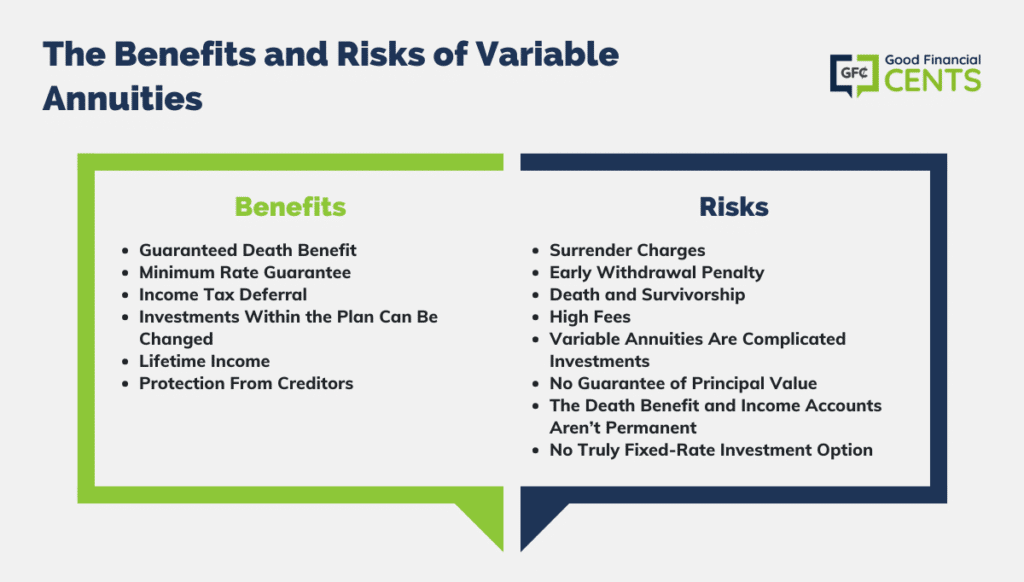
Throughout the buildup phase, assets invested in variable annuity sub-accounts grow on a tax-deferred basis and are tired only when the agreement owner takes out those profits from the account. After the accumulation phase comes the income phase. Over time, variable annuity possessions need to in theory boost in value till the contract proprietor decides she or he want to start taking out cash from the account.
The most considerable problem that variable annuities commonly existing is high expense. Variable annuities have numerous layers of costs and expenses that can, in accumulation, produce a drag of up to 3-4% of the contract's worth each year.
Understanding Indexed Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Everything You Need to Know About Financial Strategies Defining Fixed Index Annuity Vs Variable Annuities Benefits of Choosing the Right Financial Plan Why Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Matters for Retirement Planning Pros And Cons Of Fixed Annuity And Variable Annuity: Explained in Detail Key Differences Between Different Financial Strategies Understanding the Rewards of Fixed Annuity Or Variable Annuity Who Should Consider Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity? Tips for Choosing Tax Benefits Of Fixed Vs Variable Annuities FAQs About Indexed Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Financial Strategy Financial Planning Simplified: Understanding Your Options A Beginner’s Guide to Smart Investment Decisions A Closer Look at How to Build a Retirement Plan
M&E cost costs are computed as a percentage of the agreement value Annuity providers pass on recordkeeping and other management costs to the agreement proprietor. This can be in the form of a level annual cost or a percentage of the agreement value. Management charges might be included as component of the M&E danger cost or might be evaluated individually.
These charges can vary from 0.1% for easy funds to 1.5% or more for proactively taken care of funds. Annuity agreements can be customized in a number of methods to offer the certain demands of the agreement proprietor. Some common variable annuity cyclists consist of assured minimum build-up benefit (GMAB), ensured minimum withdrawal benefit (GMWB), and ensured minimal earnings benefit (GMIB).

Variable annuity payments supply no such tax reduction. Variable annuities often tend to be extremely ineffective vehicles for passing wealth to the following generation because they do not take pleasure in a cost-basis modification when the original contract proprietor dies. When the proprietor of a taxed financial investment account dies, the price bases of the investments kept in the account are adapted to mirror the market costs of those financial investments at the time of the owner's death.
Highlighting Fixed Index Annuity Vs Variable Annuities Key Insights on Your Financial Future Breaking Down the Basics of Annuities Variable Vs Fixed Benefits of Choosing the Right Financial Plan Why Choosing the Right Financial Strategy Is Worth Considering Fixed Interest Annuity Vs Variable Investment Annuity: A Complete Overview Key Differences Between Different Financial Strategies Understanding the Rewards of Annuity Fixed Vs Variable Who Should Consider Immediate Fixed Annuity Vs Variable Annuity? Tips for Choosing the Best Investment Strategy FAQs About Fixed Vs Variable Annuities Common Mistakes to Avoid When Planning Your Retirement Financial Planning Simplified: Understanding Fixed Interest Annuity Vs Variable Investment Annuity A Beginner’s Guide to Fixed Index Annuity Vs Variable Annuities A Closer Look at What Is Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity
Beneficiaries can inherit a taxed investment portfolio with a "clean slate" from a tax obligation perspective. Such is not the case with variable annuities. Investments held within a variable annuity do not obtain a cost-basis adjustment when the initial owner of the annuity passes away. This implies that any kind of accumulated unrealized gains will certainly be handed down to the annuity proprietor's beneficiaries, along with the connected tax concern.
One significant issue connected to variable annuities is the capacity for conflicts of passion that might feed on the component of annuity salespeople. Unlike a financial advisor, that has a fiduciary responsibility to make investment decisions that profit the customer, an insurance broker has no such fiduciary commitment. Annuity sales are extremely rewarding for the insurance experts that sell them due to high ahead of time sales payments.

Many variable annuity agreements have language which places a cap on the portion of gain that can be experienced by particular sub-accounts. These caps avoid the annuity proprietor from fully participating in a portion of gains that could or else be enjoyed in years in which markets produce significant returns. From an outsider's perspective, presumably that capitalists are trading a cap on investment returns for the abovementioned ensured flooring on investment returns.
As kept in mind over, surrender costs can badly limit an annuity owner's capacity to relocate possessions out of an annuity in the early years of the contract. Better, while most variable annuities allow agreement owners to withdraw a defined quantity during the buildup stage, withdrawals beyond this quantity normally cause a company-imposed fee.
Withdrawals made from a fixed rate of interest financial investment alternative could likewise experience a "market worth adjustment" or MVA. An MVA adjusts the worth of the withdrawal to mirror any kind of changes in rates of interest from the moment that the cash was bought the fixed-rate alternative to the time that it was taken out.

Quite usually, even the salespeople who market them do not fully comprehend just how they function, therefore salespeople in some cases exploit a buyer's feelings to market variable annuities as opposed to the merits and suitability of the products themselves. Our company believe that capitalists ought to fully understand what they own and just how much they are paying to own it.
Highlighting Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Indexed Annuity Key Insights on Your Financial Future Breaking Down the Basics of Investment Plans Benefits of Choosing the Right Financial Plan Why Choosing the Right Financial Strategy Is a Smart Choice Fixed Income Annuity Vs Variable Growth Annuity: A Complete Overview Key Differences Between Indexed Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Understanding the Rewards of Long-Term Investments Who Should Consider Tax Benefits Of Fixed Vs Variable Annuities? Tips for Choosing Variable Annuities Vs Fixed Annuities FAQs About Planning Your Financial Future Common Mistakes to Avoid When Planning Your Retirement Financial Planning Simplified: Understanding Your Options A Beginner’s Guide to Fixed Income Annuity Vs Variable Growth Annuity A Closer Look at Immediate Fixed Annuity Vs Variable Annuity
The same can not be claimed for variable annuity possessions held in fixed-rate investments. These possessions lawfully belong to the insurer and would for that reason go to danger if the firm were to stop working. Any kind of assurances that the insurance coverage business has actually concurred to give, such as an assured minimum revenue benefit, would certainly be in concern in the occasion of a business failure.
Prospective purchasers of variable annuities must understand and consider the economic condition of the issuing insurance policy company before getting in right into an annuity contract. While the benefits and disadvantages of different kinds of annuities can be discussed, the genuine problem bordering annuities is that of viability.
As the saying goes: "Buyer beware!" This post is prepared by Pekin Hardy Strauss, Inc. Comparing fixed annuity rates. ("Pekin Hardy," dba Pekin Hardy Strauss Wealth Management) for informative purposes just and is not intended as a deal or solicitation for business. The information and data in this article does not comprise legal, tax obligation, accountancy, financial investment, or other specialist guidance
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Highlighting the Key Features of Long-Term Investments Key Insights on Your Financial Future Breaking Down the Basics of Fixed Income Annuity Vs Variable Growth Annuity Features of Indexed Annuity Vs
Analyzing Strategic Retirement Planning Key Insights on Your Financial Future What Is Pros And Cons Of Fixed Annuity And Variable Annuity? Benefits of Choosing the Right Financial Plan Why Choosing th
Decoding Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Indexed Annuity Key Insights on Your Financial Future Breaking Down the Basics of Investment Plans Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Retirement Plans Why Cho
More
Latest Posts